Introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are under constant pressure to optimize operations, reduce manual effort, and respond swiftly to changing market demands. IFS Cloud Workflows provide a powerful, flexible framework for automating, validating, and enriching business processes across industries. By leveraging a visual, low-code environment and deep integration with business events, IFS Cloud Workflows empower IT managers and business process analysts to streamline operations, enforce business rules, and drive continuous improvement - without the need for extensive custom development .
This article explores the core concepts, architecture, key features, real-world applications, and best practices for IFS Cloud Workflows, with a focus on how they enable organizations to adjust and improve their business processes.
Core Concepts and Architecture
What Are IFS Cloud Workflows?
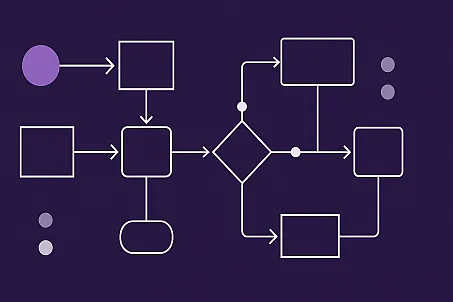
IFS Cloud Workflows are sequences of automated tasks designed to process business data, interact with users, and integrate with both internal and external systems. They are built on the Business Process Modeling Notation (BPMN) standard, ensuring clarity and alignment between business and IT stakeholders .
Types of Workflows
IFS Cloud supports three primary workflow types, each tailored to specific business needs:
| Workflow Type | Purpose | Typical Use Case | Triggered By | Timing Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Interaction | Collect additional user input | Prompting for extra data during a transaction | Projection Action | After |
| Validation | Enforce business rules and prevent errors | Blocking invalid transactions with error messages | Projection/Event Action | Before, After |
| Process Enrichment | Automate data creation/modification | Updating related records, background processing | Projection/Event Action | Before, After, Async |
1. User Interaction Workflows
- Purpose: Prompt users for additional information via forms during a business process.
- Trigger: Initiated by a specific action (Create, Read, Update, Delete, or custom action/function) within an IFS Projection.
- Integration: Presents forms to users in the IFS Cloud Web client, collects data, and uses it for further workflow decisions or system actions .
2. Validation Workflows
- Purpose: Enforce business rules and prevent users from completing actions that violate predefined criteria.
- Trigger: Can be initiated by projection actions or custom business events, either before or after a transaction.
- Integration: Displays localized error messages and halts transactions when validation fails, using the IFS Failure Event in BPMN .
3. Process Enrichment Workflows
- Purpose: Automate the creation, modification, or deletion of data as part of a business process.
- Trigger: Can be linked to projection actions or business events, with flexible timing (before, after, or asynchronously).
- Integration: Invokes internal IFS Cloud operations (CRUD, functions, actions) to enrich or modify business processes, including background jobs .
Workflow Triggers and Integration with Business Events
Workflows are tightly integrated with business events and system actions:
- Projection Actions: Attach workflows to CRUD operations or custom actions/functions, ensuring automation is triggered at the right moment.
- Event Actions: Trigger workflows in response to custom business events, such as status changes or approvals.
- Cascading Workflows: Workflows can trigger additional projections or events, enabling complex, multi-step business process automation .
Key Features and Functionality
Workflow Designer Capabilities
IFS Cloud’s Workflow Designer is a visual, low-code tool that allows users to model, configure, and deploy workflows using BPMN:
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: Easily create and modify workflows with a graphical interface, accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
- Version Control: Deployed workflows are version-locked for stability and traceability.
- Simulation and Troubleshooting: Simulate execution, inspect paths, and debug issues before deployment.
- Monitoring: Record workflow inputs and view execution logs for performance optimization .
User Interaction Forms
- Customizable Forms: Design forms to collect specific data from users during workflow execution.
- Multi-Step Interactions: Guide users through sequences of tasks, ensuring all necessary information is gathered.
- Validation: Include logic to ensure data quality and completeness before submission .
Automation Features
- Elimination of Manual Tasks: Automate repetitive, low-value activities, freeing up human resources for strategic work.
- Process Enrichment: Automatically create, update, or delete data as part of a transaction.
- Validation Workflows: Prevent invalid actions and enforce business rules without custom code.
- Asynchronous Processing: Run background jobs (e.g., sending emails) without blocking main processes.
- Advanced Customization: Use workflow commands and custom event triggers for high flexibility .
Integration Points
- Event-Driven Automation: Link workflows to business events and projection actions for real-time process automation.
- Native IFS Integration: Seamlessly connect with all IFS Cloud modules (finance, supply chain, manufacturing, etc.).
- External System Connectivity: Integrate with external applications via APIs and standard protocols.
- AI and IoT Integration: Embed AI/ML and IoT data for intelligent, real-time automation .
Summary Table: Workflow Types and Use Cases
| Workflow Type | Typical Use Case | Triggered By | Timing Options |
|---|---|---|---|
| User Interaction | Prompting for extra data during a transaction | Projection Action | After |
| Validation | Blocking invalid transactions with error messages | Projection/Event Action | Before, After |
| Process Enrichment | Updating related records, background processing | Projection/Event Action | Before, After, Async |
Real-World Examples
Example 1: Manufacturing – Streamlining Operations and Decision-Making
Scenario:
A group of manufacturing companies sought to modernize their ERP systems to boost efficiency and productivity. By implementing IFS Cloud Workflows, they automated routine tasks, integrated real-time data collection, and enabled seamless data migration from legacy systems.
Workflow Implementation:
- Automated repetitive tasks such as inventory updates and production scheduling.
- Integrated real-time data from shop floor sensors into workflows for immediate decision-making.
- Used validation workflows to enforce quality checks before products moved to the next stage.
Outcomes:
- Significant improvements in operational efficiency and productivity.
- Reduced manual intervention and errors.
- Enhanced decision-making capabilities due to real-time insights .
Example 2: Construction – Enhancing Project Management and Financial Processes
Scenario:
Large construction firms faced challenges managing complex project and financial workflows. With IFS Cloud, they automated project management tasks, approvals, and financial reconciliations.
Workflow Implementation:
- Automated approval processes for project milestones and budget changes.
- Integrated workflows with business events to trigger notifications and document generation.
- Used process enrichment workflows to update related records and ensure data consistency across modules.
Outcomes:
- Improved project management and financial process efficiency.
- Reduced errors and improved operational transparency.
- Better, data-driven decision-making through real-time workflow-triggered insights .
Best Practices for Designing and Implementing Effective Workflows
1. Start with a Clear Business Objective
- Define the business process to automate or improve.
- Identify pain points, desired outcomes, and KPIs.
- Prioritize simplicity - start with high-impact, simple workflows .
2. Leverage Workflow Types Appropriately
- Use User Interaction workflows for processes requiring user input.
- Apply Validation workflows to enforce business rules and data quality.
- Employ Process Enrichment workflows for data modification and background processing .
3. Utilize Workflow Designer and Templates
- Take advantage of the visual Workflow Designer for building, testing, and deploying workflows.
- Use template workflows for common scenarios to accelerate development .
4. Integrate with Business Events and Projections
- Attach workflows to specific projection calls or CRUD operations.
- Use data and call action types to ensure correct triggers .
5. Focus on Data Quality and Governance
- Validate and enrich data early in the process.
- Assign data stewards and define protocols for data quality and compliance .
6. Test, Monitor, and Optimize
- Use troubleshooting mode and execution logs to debug and optimize workflows.
- Regularly review performance and user feedback for continuous improvement .
7. Document and Train
- Maintain up-to-date documentation for each workflow.
- Incorporate workflow usage and troubleshooting into user training programs .
8. Adopt a Data-First and Governance-Driven Approach
- Integrate data strategy and governance into workflow design.
- Migrate only clean, deduplicated data during system upgrades .
9. Leverage Automation and Integration Features
- Identify and automate repetitive manual tasks.
- Integrate with external systems using REST APIs and script tasks .
Conclusion
IFS Cloud Workflows offer a comprehensive, flexible, and scalable solution for automating, validating, and enriching business processes. By leveraging visual design tools, deep integration with business events, and robust automation features, organizations can:
- Eliminate manual tasks and reduce errors.
- Accelerate process completion and improve quality.
- Enhance business agility and compliance.
- Lower operational costs and improve customer satisfaction .
Recommendations for Organizations:
- Start with process mapping and analysis to identify automation opportunities.
- Engage cross-functional teams in workflow design.
- Use the Workflow Designer and templates for rapid development.
- Monitor, measure, and optimize workflows continuously.
- Provide training and maintain documentation to ensure adoption and sustainability.
As digital transformation accelerates, IFS Cloud Workflows will be a key enabler for organizations seeking to maintain competitiveness, drive innovation, and achieve operational excellence .
Appendix: Workflow Types and Use Cases Table
| Workflow Type | Purpose | Typical Use Case | Triggered By | Timing Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Interaction | Collect additional user input | Prompting for extra data during a transaction | Projection Action | After |
| Validation | Enforce business rules and prevent errors | Blocking invalid transactions with error messages | Projection/Event Action | Before, After |
| Process Enrichment | Automate data creation/modification | Updating related records, background processing | Projection/Event Action | Before, After, Async |
This article is based on the official IFS Cloud documentation and reputable industry sources. For further details, refer to the IFS Cloud Business Process Automation Documentation and related resources.

Executive Summary
Strategic application of IFS Cloud customizations can significantly enhance operational efficiency, user adoption, and data-driven decision-making. When executed within a structured DMAIC framework and aligned with MECE principles, customizations yield measurable business value while maintaining system integrity.
Key takeaways:
-
High ROI potential in targeted areas: UI personalization, workflow automation, and enriched data models.
-
Critical success factors include stakeholder alignment, rigorous testing, and staged deployment.
-
Risks - such as scope creep, performance degradation, or compliance issues - must be mitigated via robust governance and continuous improvement cycles.
DMAIC Breakdown (MECE-Structured)
1. Define – Problem Statement & Objectives
Problem: Standard IFS Cloud functionality may not fully reflect unique business processes, leading to inefficiencies, manual workarounds, and suboptimal reporting.
Objectives:
-
Enhance user productivity through UI customization (dashboards, branding).
-
Improve operational efficiency via custom workflows & automation.
-
Strengthen reporting & compliance with extended data models.
Scope:
-
Focus on three distinct customization areas (UI, Business Logic, Data Model).
-
Limit changes to those delivering measurable business process improvements.
2. Measure – Baseline Metrics & KPIs
Key Metrics (Pre-Customization Baseline):
-
User task completion time (min/transaction).
-
Error rates in manual processes (%).
-
Data completeness & accuracy (%).
-
User adoption rates (% active usage vs. total licensed).
-
Report generation time (min).
Measurement Plan:
-
Use system logs to establish baseline performance.
-
Capture qualitative feedback from key user groups.
-
Benchmark against similar ERP deployments in industry.
3. Analyze – Gaps & Root Causes
UI Customizations – Gaps
-
Standard dashboards lack role-specific KPIs → delays in decision-making.
-
Generic theming reduces user engagement & familiarity.
Business Logic – Gaps
-
Manual workflows in procurement & approvals create bottlenecks.
-
Repetitive data entry leads to errors & low morale.
Data Model – Gaps
-
Missing fields for compliance-specific reporting.
-
Weak entity relationships hinder cross-department analytics.
Root Causes:
-
One-size-fits-all ERP configuration.
-
Insufficient alignment between ERP standard processes & actual business workflows.
-
Limited awareness of IFS customization capabilities.
4. Improve – Solutions & Recommendations
UI Enhancements
-
Deploy custom role-based dashboards (Ops, Finance, SCM).
-
Apply corporate branding for familiarity and faster adoption.
Business Logic Enhancements
-
Automate recurring approval flows in procurement and expense management.
-
Implement error-checking scripts to reduce data entry mistakes.
Data Model Enhancements
-
Add custom compliance fields to supplier master data.
-
Define new relationships between customer orders and service contracts for better lifecycle analysis.
Quick Wins (≤3 months)
-
Custom dashboards.
-
Simple workflow automations.
-
Low-complexity field additions.
Long-Term Initiatives (>6 months)
-
Complex data model restructuring.
-
Enterprise-wide automation strategy.
5. Control – Governance & Sustainability
Governance Mechanisms:
-
Establish a Customization Steering Committee for change approvals.
-
Maintain a Customization Registry documenting scope, owner, and dependencies.
Testing & Deployment:
-
Apply User Acceptance Testing (UAT) in a sandbox environment.
-
Use staged deployment to control risk.
Continuous Improvement:
-
Quarterly reviews of customization ROI.
-
User feedback loops via surveys and focus groups.
-
Align customization roadmap with IFS Cloud release cycles to ensure compatibility.
| Risk | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Scope creep | Budget/time overrun | Use strict change control |
| Performance degradation | Reduced system speed | Test load impact before deployment |
| Compliance breaches | Regulatory fines | Involve compliance in requirements |
| User resistance | Low adoption | Early stakeholder involvement + training |
Introduction
If you’ve ever been part of a data project, you’ve likely seen this scenario:
The technical team is sketching complex diagrams, mapping out databases and relationships.
Meanwhile, the governance team is knee-deep in policies, ownership charts, and compliance requirements.
It can feel like two entirely separate worlds - but in reality, without each other, both will fail.
In the context of IFS Cloud implementations, the interplay between data modeling and data governance is not just important - it’s essential for long-term success.
What is Data Modeling?
Think of data modeling as the blueprint of your ERP data architecture.
In IFS Cloud, this means defining:
-
Data entities (e.g., Customers, Orders, Products)
-
Attributes within each entity (e.g., Customer Name, Order Date, Product Price)
-
Relationships between entities (e.g., One customer can place many orders)
Without a clear blueprint, every module or business unit risks building its own version of the “data house,” leading to duplicated records, mismatched definitions, and reporting chaos.
And Data Governance?
Data governance is the rulebook for managing and maintaining that blueprint over time.
In an IFS Cloud environment, it determines:
-
Who can access which data (permission sets, role-based access control)
-
What data standards must be followed (naming conventions, master data rules)
-
How data is kept clean and compliant (validation rules, periodic audits)
Without governance, even the most elegant ERP data model will degrade - duplicate customers creep in, old product codes linger, and regulatory compliance is put at risk.
Where the Magic Happens - Integration
The real value comes when data modeling and data governance operate in a continuous loop:
-
Governance guides modeling: Ensuring IFS Cloud configuration follows agreed definitions, compliance requirements, and quality standards.
-
Modeling enables governance: Providing the structure for tracking data lineage, monitoring quality, and enforcing policy.
It’s not a one-time project phase - it’s an iterative cycle:
Governance → Modeling → Governance → repeat.
Why This Matters for IFS Cloud Projects
When modeling and governance are aligned from the start:
-
A common “data language” emerges across modules and teams.
-
Compliance is built in - no scrambling before audits.
-
Data quality issues are easier to detect and resolve.
-
Decision-making accelerates because reports are based on trusted data.
In short, your ERP stops being a repository of inconsistent records and becomes a reliable business asset.
A Practical Takeaway for Your Business
If your data governance efforts feel stuck, look at your ERP data models.
If your data models are out of date, review your governance processes.
The truth is simple: You can’t fix one without the other.
In IFS Cloud projects, treating data modeling and governance as independent silos is a recipe for long-term inefficiency.
Final Thought
Data modeling and data governance are the unsung power couple of IFS Cloud implementations.
When they work together, your ERP becomes more than just a system - it becomes a trusted foundation for business growth.