Introduction
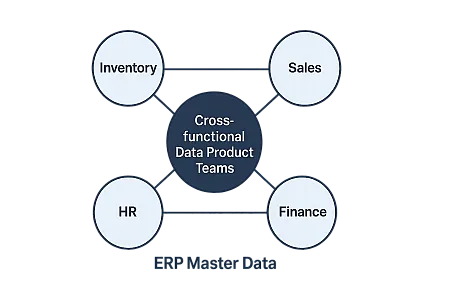
Data Mesh is a new way for organizations to manage and use data. Instead of having one big, central team handle all the data, Data Mesh lets different business teams own and manage their own data. This approach helps make data more useful, trusted, and available across the company. One of the most important steps in making Data Mesh work is building cross-functional data product teams. These teams bring together individuals with diverse skills to work toward a shared goal. When done right, they help break down barriers, improve data quality, and make the business more agile
.
What are Cross-functional Data Product Teams?
A cross-functional data product team is a group made up of people from different departments and backgrounds. Each person brings their own skills and knowledge. For example, a team might include data engineers, analysts, product owners, and business experts. Data engineers handle the technical side, analysts make sense of the data, product owners guide the team’s direction, and business experts make sure the data meets real business needs
. By working together, these teams can create and manage data products that are useful and reliable.For example, if a company wants to improve its sales data, a cross-functional team might include a sales manager, a data engineer, a business analyst, and a product owner. Each person helps make sure the data product is accurate, useful, and easy to use.
Key Activities and Best Practices
- Bringing Together Diverse Skills: Start by choosing team members from different areas, such as IT, business, and analytics. Ensure that each person understands their role and how they can contribute to the team's success.
- Full Responsibility for Data Products: Give the team ownership of their data product from start to finish. This means they are responsible for creating, maintaining, and improving the data product over time.
- Close Collaboration: Encourage the team to work closely with both business and technical sides. Regular meetings and open communication help everyone stay on the same page.
- Best Practices for Team Setup: Set clear goals and processes. Use tools like Agile or Scrum to help the team work in short, focused cycles. Make sure everyone can give and receive feedback openly
.
- Ongoing Support: Provide training and resources so the team can keep learning and improving.
Challenges and Solutions
- Unclear Roles: Sometimes, team members are unsure of their job responsibilities. Solve this by clearly defining each person’s role and responsibilities from the start
.
- Poor Communication: Teams can struggle if they don’t talk enough. Set up regular meetings and use shared tools to keep everyone informed.
- Lack of Trust: People from different backgrounds may not trust each other at first. Build trust by encouraging open feedback and celebrating team successes.
- Resistance to Change: Some people may be used to working in silos. Help them see the benefits of working together by sharing early wins and positive results.
Data Governance Considerations
Data governance is about making sure data is managed safely and adequately. In cross-functional teams, it’s essential to establish clear guidelines regarding who owns the data, who has access to it, and how it should be utilised. Each team should follow company-wide standards for privacy, security, and quality. This helps keep data safe and reliable, even as teams work more independently.
Business and Cultural Impact
Cross-functional teams help break down silos between departments. This leads to better collaboration and faster decision-making. When teams own their data products, they care more about quality and results. This supports business goals by making data more useful and trusted. Over time, this approach builds a culture of ownership, teamwork, and continuous improvement.
Practical Tips and Checklist
Tips:
- Start small with one or two teams before expanding.
- Choose team members who are open to learning and working with others.
- Set clear goals and celebrate early successes.
- Provide training on both technical and business topics.
Checklist:
- Team members from different departments are included
- Roles and responsibilities are clearly defined
- Regular meetings are scheduled
- Data governance rules are in place
- Team has access to the needed tools and training
Conclusion
Forming cross-functional data product teams is a key step in the Data Mesh journey. These teams bring together different skills and viewpoints, helping to break down barriers and improve data quality. By giving teams ownership and support, organizations can make their data more valuable and trusted, setting the stage for long-term success with Data Mesh
.
Introduction
Data Mesh is a new way for organizations to manage and use data. Instead of having a single, central team handle all the data, Data Mesh allows different business teams to own and manage their own data. This makes data more useful, trusted, and available across the company. One of the first and most important steps in Data Mesh is to identify data domains. Finding and defining these domains helps teams work more effectively and ensures that everyone knows who is responsible for each set of data.
What is Identifying Data Domains?
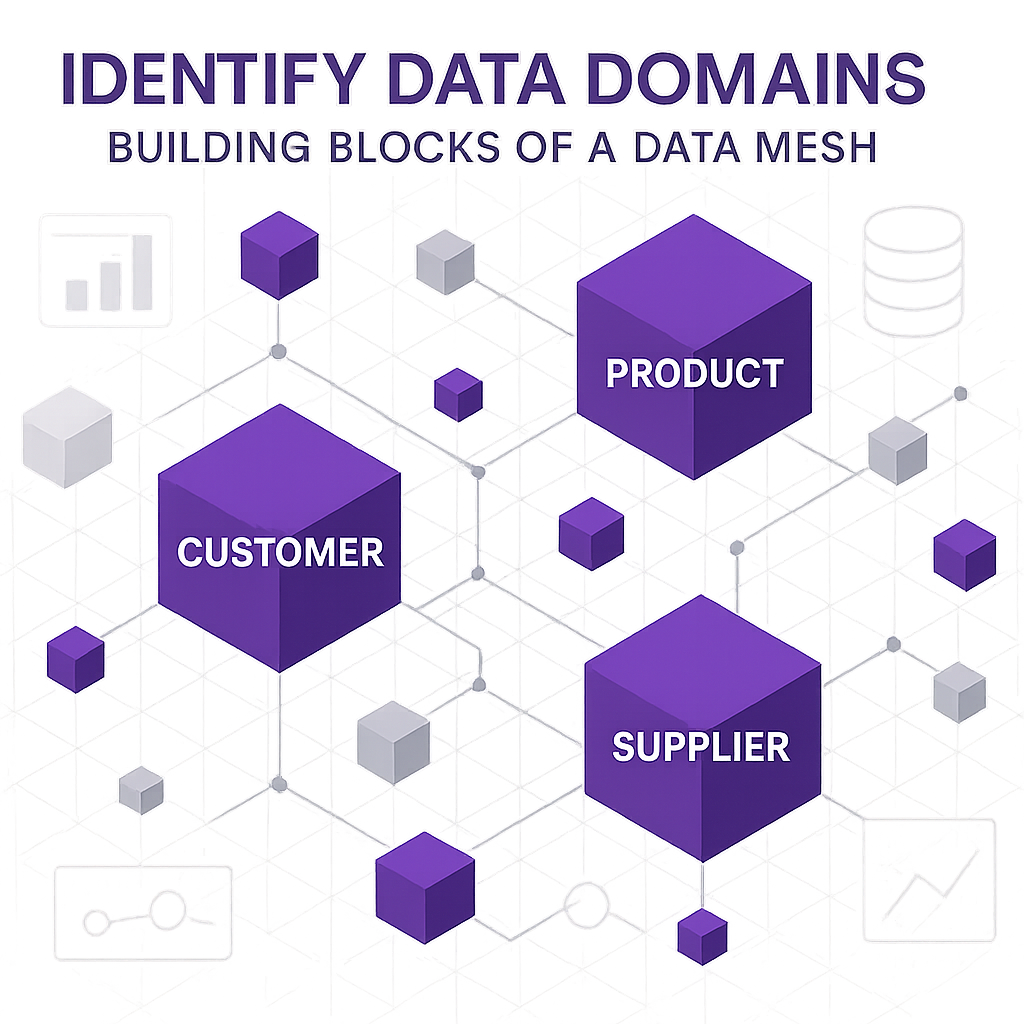
A data domain is a group of related data that corresponds to a specific business function, such as Sales, Finance, or Operations. In Data Mesh, each domain is treated like a product. This means the team in charge of the domain is responsible for ensuring the data is of high quality and easy to use for others within the company.
For example, the Sales domain might include all the data about customers, orders, and revenue. The Finance domain could include budgets, expenses, and payments. By breaking data into domains, companies can make sure the right people are in charge of the right data.
Key Activities and Best Practices
- Break Down the Company into Business-Aligned Domains:
Start by looking at how your business is organized. Each major area, like Sales, Marketing, or HR, can be a domain. Consider the data each team uses and creates on a daily basis.
- Assign Clear Ownership and Accountability:
Each domain should have a team that owns it. This team is responsible for the quality, security, and sharing of the data. The domain owner acts like a product owner, making sure the data meets the needs of others.
- Start with High-Impact Domains:
Begin with domains that have the biggest effect on your business. For example, if customer data is very important, start with the Sales or Customer domain. This helps show quick wins and builds support for Data Mesh.
- Define and Refine Domains Over Time:
Domains are not set in stone. As your business changes, you may need to split, merge, or adjust domains. Review domains regularly to make sure they still make sense for your company.
Challenges and Solutions
- Overlapping Domains:
Sometimes, two teams may want to own the same data. To solve this, talk with both teams and agree on clear boundaries. Use contracts to define who provides what data and how it is shared.
- Unclear Ownership:
If no one wants to own a domain, it can lead to poor data quality. Make sure every domain has a clear owner and that their role is understood and supported by leadership.
- Changing Business Needs:
As your company grows, domains may need to change. Be flexible and review domains often to keep them aligned with business goals.
Data Governance Considerations
Data governance is about establishing rules and ensuring that everyone follows them. In Data Mesh, each domain team must follow company-wide regulations for privacy, security, and data quality. The domain owner is responsible for making sure their team follows these rules. At the same time, there should be a central group that helps set standards and checks that domains are working together smoothly.
Business and Cultural Impact
Clear data domains enable teams to work more effectively together. When everyone knows who owns what data, it is easier to find answers and solve problems. This leads to improved data quality and enables the business to make faster, more informed decisions. It also fosters a culture where teams take responsibility for their data and are proud to share it with others.
Practical Tips and Checklist
Tips:
- Begin by creating a map of your business areas and the data they utilise.
- Consult with business leaders to determine which domains are most important.
- Assign a clear owner to each domain.
- Write down the rules for each domain, including what data it covers and who can use it.
- Review domains regularly and adjust as needed.
Checklist:
- List all major business areas.
- Identify the main data used and created by each area.
- Assign a domain owner for each area.
- Set clear rules and responsibilities.
- Review and update domains as the business changes.
Conclusion
Identifying data domains is a key step in building a Data Mesh. It helps teams take ownership of their data, improves quality, and makes it easier for everyone to find and use the data they need. By starting with clear domains, your company can move forward on the Data Mesh journey with confidence and success.
.
Introduction
A Data Mesh is a new approach for organizations to manage and utilize their data. Instead of having one central team in charge of all data, Data Mesh gives different business teams the power to own and operate their data. This approach helps make data more useful, trusted, and available across the company. Starting your Data Mesh journey with a clear vision and strategy is the most crucial step. It sets the direction, helps everyone understand the goals, and makes sure all teams are working together from the start.
What is Defining Vision and Aligning Strategy?
Defining a vision means deciding what you want to achieve with Data Mesh. It’s about setting a clear goal for how data should help your business. Aligning strategy means making sure this vision matches your company’s main goals and plans. For example, if your company wants to deliver products faster, your Data Mesh vision might focus on making data easier to find and use so that teams can make quicker decisions. This step is about making sure everyone understands why you are moving to Data Mesh and what success will look like.
Key Activities and Best Practices
- Assess the Current State of Data: Start by looking at how your company currently manages data. Find out who owns which data, how data is shared, and where there are problems or gaps.
- Find Pain Points, Tech Debt, and Data Silos: Identify where data is hard to access, where teams are working in isolation, or where old systems are causing problems. These are the areas where Data Mesh can help the most.
- Connect Vision to Business Objectives: Make sure your Data Mesh vision supports your company’s main goals. For example, if your business wants to improve customer experience, your vision should focus on making customer data more reliable and accessible.
- Get Executive Support and Funding: Leadership support is key. Leaders need to understand the value of Data Mesh and be willing to invest in the changes required.
- Build a Shared Vision: Use workshops and open discussions to get input from different teams. Make sure everyone understands the benefits and their role in the new approach. Use tools like the Lean Value Tree to map out your vision, goals, and how you’ll measure success.
Challenges and Solutions
- Lack of Buy-In: Some teams may not see the value or may fear change.
- Solution: Communicate clearly about the benefits and involve teams early in the process.
- Unclear Goals: Without a clear vision, teams may pull in different directions.
- Solution: Use simple, shared language to describe your vision and goals. Make sure everyone agrees on what success looks like.
- Resistance to Change: People may be used to the old way of working.
- Solution: Offer training, support, and incentives for teams taking on new roles.
Data Governance Considerations
Data governance is about making sure data is managed properly, securely, and ethically. In Data Mesh, governance is shared across teams, not controlled by one central group. Each team is responsible for the quality and security of its own data products. Clear rules and responsibilities help everyone know what is expected and keep data trustworthy.
Business and Cultural Impact
A clear vision and strategy help build trust across the business. When everyone knows the goals and their role, it’s easier to share data and work together. This leads to better data quality, faster decision-making, and a culture where teams feel ownership and pride in their data. Over time, this supports innovation and helps the business grow.
Practical Tips and Checklist
Tips:
- Start with the organizational boundaries you already have.
- Use simple tools like the Lean Value Tree to map out your vision and goals.
- Communicate openly and often with all teams.
- Be flexible and ready to adjust your approach as you learn and grow.
Checklist:
- Have you defined a clear vision for Data Mesh?
- Is your vision aligned with business goals?
- Have you identified current data challenges and opportunities?
- Do you have executive support and funding?
- Have you involved all key teams in the planning process?
- Are roles and responsibilities clear?
- Is there a plan for ongoing communication and learning?
Conclusion
Defining vision and aligning strategy is the foundation of a successful Data Mesh journey. It ensures everyone is working toward the same goals and sets up your organization for long-term success. By starting with a clear vision, aligning with business objectives, and involving all teams, you create a strong base for the next steps in your Data Mesh transformation.
TL;DR - A golden record is the authoritative, single‑source version of your most valuable data (customers, products, suppliers, etc.). Establishing one boosts decision quality, unlocks operational efficiency, and de‑risks compliance. This playbook shows business leaders how - and why - to make it happen.
What Is a Golden Record?
A golden record is “a single, well‑defined version of all the data entities in an organizational ecosystem,” essentially the single source of truth[1]. It sits at the heart of Master Data Management (MDM), reconciling and enriching duplicate records scattered across CRM, ERP, and other systems until one trusted profile remains.
A golden record provides the complete 360‑degree view of an entity - nothing missing, nothing duplicated, always current.
Why Business Leaders Should Care
- Growth & Insight. In the latest Dun & Bradstreet B2B Data Report, 81 % of senior decision‑makers said data’s primary mission is to fuel growth - but only 57 % trust their data to do so[3].
- Quality & Cost. HFS Research finds 40 % of enterprise data is “bad or unusable,” draining 25‑35 % of potential value[4].
- Compliance & Risk. One clean record per customer simplifies GDPR “right to be forgotten” actions and slashes duplicate communications.
- Operational Efficiency. Staff stop reconciling spreadsheets; systems integrate faster; analytics stop second‑guessing which number is right.
How Golden Records Are Created
The workflow is straightforward, even if the tooling is sophisticated:
- Ingest. Pull data from every relevant source system.
- Clean & Standardize. Fix format issues and obvious errors.
- Match. Use deterministic keys and fuzzy logic to find duplicates.
- Merge / Survivorship. Apply rules (or ML) to keep the “best” value for each attribute.
- Publish. Feed the mastered record back to consuming systems and analytics.

Common Challenges (and Fixes)
| Challenge | Counter‑move |
|---|---|
| Poor data quality at the source | Automate validation and enforce standards before data hits the hub. |
| Duplicate & conflicting records | Invest in robust matching algorithms and clear survivorship rules. |
| Integration complexity | Use an MDM platform or data fabric to abstract away source‑system quirks. |
| Governance fatigue | Assign data stewards and make KPIs (e.g., % duplicates) visible to execs. |
Golden Records in Action
Customer 360° View
A retailer merged marketing, e‑commerce, and support data into one golden customer profile. Result: a 19 % lift in first‑call resolution and personalized campaigns that drove a 12 % revenue uptick.
Product Data Consolidation
A manufacturer unified engineering specs, procurement costs, and sales descriptions. New products now launch in weeks, not months, because every channel reads from the same catalog.

Unified Supplier & Compliance Data
Aggregating finance, legal, and operations data into a golden supplier record simplified compliance reporting and reduced risk.
Getting Started
- Pick one domain (often customer) and run a proof‑of‑value.
- Define success KPIs: duplicate rate, time‑to‑insight, compliance effort saved.
- Select MDM tooling that supports matching, survivorship, and governance.
- Assign data owners and iterate - golden records are a living asset.
Bottom line: The golden record transforms raw, fragmented data into a strategic asset that drives growth, efficiency, and trust. In an age where data is currency, one clean record is worth more than a thousand conflicting ones.

Data governance is a set of policies, processes, and procedures that ensure the availability, security, and integrity of data throughout its entire lifecycle, from creation to disposal. It is a framework for managing data in a way that aligns with business objectives, while ensuring the highest standards of quality, security, and compliance.
Key Components of Data Governance
1. Data Quality: Ensuring data accuracy, completeness, and integrity, through processes such as data validation, data cleansing, and data normalization.
2. Data Security: Protecting data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure, through measures such as encryption, access controls, and auditing.
3. Data Integrity: Ensuring that data is complete, accurate, and consistent, with regular backups and versioning.
4. Data Confidentiality: Ensuring that data is handled and processed in accordance with organizational data protection policies and applicable laws and regulations.
Governance Process
1. Data Management: Establishing policies and procedures for the management of data, including data discovery, data ingestion, and data stewardship.
2. Stakeholder Engagement: Involving stakeholders in the governance process to ensure that their needs and expectations are met, and that they are aligned with the organization's objectives.
3. Monitoring and Auditing: Regularly reviewing and auditing data management processes to ensure compliance with policies, procedures, and standards.
Goals of Data Governance
1. Ensure data quality: Ensure that data is accurate, complete, and consistent.
2. Protect data security: Protect data from unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
3. Ensure data integrity: Ensure that data is complete, accurate, and consistent, with regular backups and versioning.
4. Support business objectives: Ensure that data is used to support business objectives, such as decision-making, risk management, or regulatory compliance.
5. Improve business outcomes: Ensure that data is used to drive business outcomes, such as revenue growth, customer acquisition, or efficiency improvements.
Benefits of Data Governance
1. Improved decision-making: Ensures that data is used to inform business decisions.
2. Increased efficiency: Reduces waste and improves productivity.
3. Enhanced customer experience: Ensures that customer data is used to deliver personalized experiences.
4. Better compliance: Ensures that data is handled and processed in compliance with applicable regulations and standards.
5. Increased confidence: Ensures that stakeholders have confidence in the quality and security of the data.